by Ali Hendren
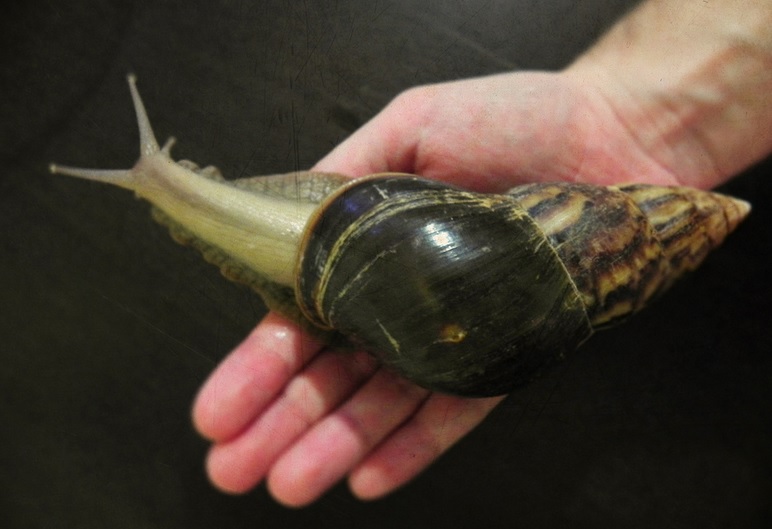
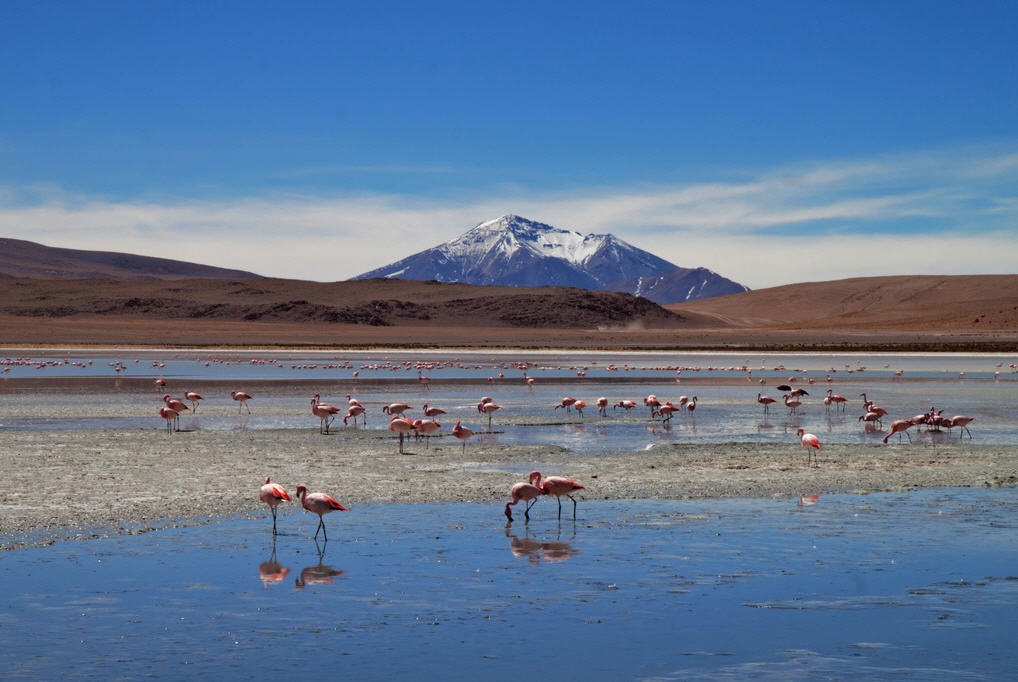
In 1988 at an agribusiness expo in Curitiba in southern Brazil, giant African land snails (Achatina fulica) were heralded as a promising new food source to replace smaller escargot snails. The introduction at the fair was so widely advertised and aggressively marketed that commercial breeders, cooperatives and even private homeowners began rearing the snails–endemic to eastern Africa–immediately with kits sold at the expo.
“The snails were supposed to represent social and economic progress for Brazil,” says Roberto Vogler, an Argentine scientist who studies the snails along the border his country shares with Brazil. “They were going to position the country as the world’s leading supplier of escargot.”
But a booming escargot market in Brazil never materialized. Many of the smaller producers had neither the means to properly process the meat nor the public demand to drive a now flooded market. Frustrated with their failed investment, operations were abandoned and snails were released into the wild in overwhelming numbers.
Today, the infestation has spread throughout Latin America–and not at a snail’s pace. They’ve invaded 24 of Brazil’s 26 states, spread through Venezuela and Colombia and have breached the borders of Paraguay, Argentina, Ecuador and Peru–posing both an agricultural and a public health threat. The snails are sweeping the continent carrying parasites and an appetite for most any crop.
The snails’ pace
On paper, the introduction of A. fulica for escargot farming in Brazil appeared promising. The snails are larger Continue reading “Giant African land snails are invading Latin America”